A Phase 0 study accelerates drug development and takes place before you start your Phase 1 trial. At TRACER, we often get the question “How long is Phase 0 in clinical trials?”
Even though a Phase 0 study is seen as an extra step, it will actually speed up your Phase 1, 2, and 3 trials. In this blog, we go over how long a Phase 0 study in clinical trials can take. What steps are involved and more importantly, how can a Phase 0 study save you time and resources in later, more expensive phases of clinical development?
In short: How long is Phase 0 in clinical trials?
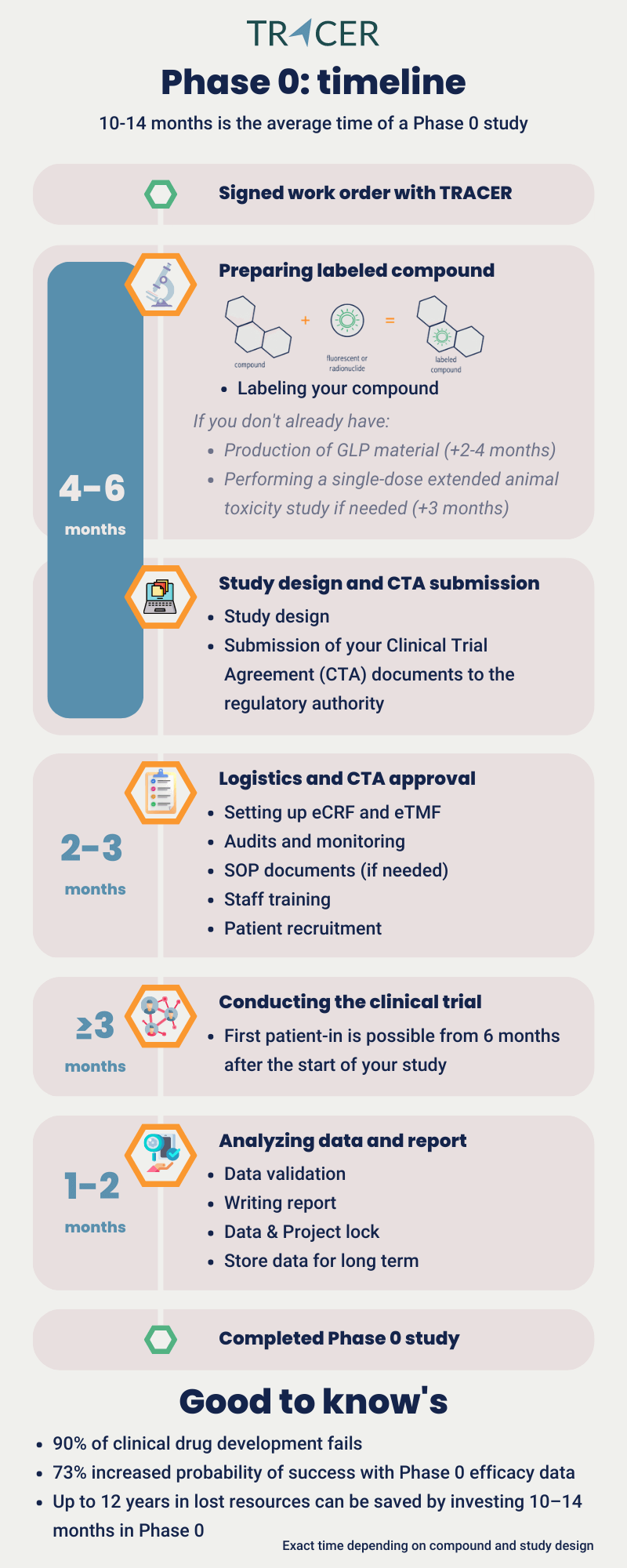
Phase 0 in clinical trials takes about 10-14 months. This is the time from signing off on the project to closing the study. Although a Phase 0 study itself often only takes a few months, additional time is needed to complete regulatory and logistic-related activities. The exact time a Phase 0 study takes depends mainly on three factors:
- 1. Your targeted disease
- 2. The type of drug you are developing
- 3. The design of your clinical study
Don’t hesitate to contact us, we gladly meet to give you an estimate for your pipeline.
Preparing and labeling your compound for Phase 0
The first step, preparing and labeling your compound takes an average of 4-6 months. For the Phase 0 clinical trial, GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) material is needed. If you don’t have GLP material yet, we can help you with that. This takes approximately an additional 2-4 months. You don’t need GMP material yet. When coupling your compound with a radionuclide or fluorescent dye, we do this under GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) conditions. During these 4-6 months we can already design your study protocol.
Prevent duplicate investments
Contacting us in an early phase of your drug discovery and development can prevent duplicate investments. We will make your drug ready for the in-human clinical trial, without you having to invest in GMP costs beforehand. Another example of how you can save costs is the single-dose extended toxicity study.
Single dose extended toxicity study for clinical trial Phase 0
It’s important to keep in mind that you don’t need to invest in a full toxicity study for your compound. When working with TRACER we will couple your compound with a tracer for molecular imaging. There are many tracers to choose from depending on the binding properties of your compound and the target tissue of your interest. Depending on the existence of data on toxicity levels for your compound and the coupled tracer, we will need to do a single-dose extended toxicity study. If tox data is not available, this step takes an additional 3 months.
Good to know: a single-dose extended toxicity study is about 20% of the costs in comparison to a full toxicity study.
Clinical Trials Application (CTA)
After signing your contract with TRACER, we start planning the study. From preparing your (labeled) investigational medicinal product (IMP) production and writing the necessary documents up to the submission of your study to the regulatory authorities. This includes a clinical trial design based on your requirements and study goals.
After finalizing your study documentation, it takes 2-3 months to receive regulatory approval for clinical trials executed in the Netherlands. We use this waiting period to set up study logistics so that your project can start directly after CTA approval.
How much time does logistics take?
Logistics in clinical trials include contacting all stakeholders, conducting audits, assigning monitoring, training staff, and setting up the eCRF and eTMF. The eCRF stands for electronic Case Record Form and is used for collecting participant data. The eTMF is the electronic Trial Master File for managing all essential trial documents. This whole part takes 2-3 months and includes the time to find patients for your clinical trial.
Patients in Phase 0 study
The logistics of a Phase 0 study include the recruitment of participants. For a Phase 0 clinical trial patients with the target of interest are recruited. What you need to keep in mind, is that, depending on your therapeutic area, finding patients may take time. Compared to all 4 phases of clinical trials, you need the least number of patients in Phase 0. Usually, 5-10 patients are sufficient. This means it usually doesn’t take long to recruit and complete your study. Expect the first patient-in from 6 months after starting your study.
Starting your Phase 0 clinical trial
The study start date is scheduled after the study has been set up, CTA has been approved and the patients have been selected. By doing a dry run with all stakeholders we make sure everything is checked. After this, your clinical trial can start. How long does the conduction of a Phase 0 clinical trial take? The study itself may take at least 3 months depending on your study protocol and the recruitment rate. After that, 1-2 months are needed to process the acquired data. We then validate your data which means the study can be locked and closed. After the study is closed, a manuscript and report can be written.
The time a Phase 0 study takes in total
How long is Phase 0 in clinical trials? A Phase 0 executed by TRACER takes in total approximately 10-14 months. The time you invest to conduct a Phase 0 trial can shorten the timeline of your subsequent clinical trials. In the following paragraphs, you’ll read how positive PK/BD data can be used.
In case your Phase 0 outcome shows that the target tissue is not reached, it will save you time and investment in other clinical trials altogether.
Continue reading about the purpose of Phase 0 in clinical trials and the effect it has on Phase I-III.
Purpose of Phase 0 clinical trial
The purpose of a Phase 0 clinical trial is to study pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and on and off-target accumulation of your compound. You will know if there is high uptake in the targeted tissue and low uptake in healthy tissue. Obtaining this data has multiple effects that save time and resources in further clinical trials.
In case the target tissue is not reached or there is high uptake in healthy tissue, it allows you to optimize your compound. Doing that at this point will prevent you from spending time and resources on non-efficient compounds that will likely fail in a later stage of clinical trials. You can use your saved time and resources on more promising compounds in your pipeline or on adapting your lead compound.
How long does each clinical phase take?
You now know how much time a Phase 0 clinical trial on average takes. You also understand the process. But how can you save time in the next stages of clinical development with your Phase 0 study data? Let’s look at how long each clinical phase takes.
Phase 1 takes around 1-2 years
How long is Phase 1 clinical trial? It takes around 1-2 years. What is Phase 1 clinical trial? The Phase 1 clinical trial design involves a larger number of healthy participants. The aim is to test the safety and tolerability of your drug. It will also check pharmacokinetics and shows how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Your Phase 0 results already gave you indicative information on this, meaning going into Phase 1 with fewer errors.
Difference Phase 1 – 0
Although Phase 1 sounds similar to Phase 0, there is a big difference. As Phase 1 is only conducted in healthy volunteers, it does not mean the pharmacokinetics will be the same in your target population. Also, a Phase 1 study doesn’t reveal the organ distribution of your drug. So how does Phase 0 help with Phase 1? First of all, it can prevent you from going into Phase 1 with an ineffective compound. Second, you can skip large animal models. Your Phase 0 study data is more relevant than any animal models.
Phase 2 takes around 2-3 years
In Phase 2 a larger number of patients with the targeted disease will participate. The aim of Phase 2 is to evaluate efficacy and side effects. The data obtained in your Phase 0 comes into use here. The Phase 0 study with molecular imaging from TRACER already visualized target engagement, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution.
The impact of Phase 0 on Phase II
Your Phase 0 results give you an understanding of the binding of your compound on diseased cells. Because you’ve already studied your compound’s in-patient behavior, you know what characteristics to look for in patient selection. The right cohort has a huge effect on clinical trials. It can rule out false results where you see no therapeutic effect on patients that didn’t express the target.
Read our blog about the benefits of molecular imaging in Phase 2 or 3.
Phase 3 takes around 2-4 years
Phase 3 takes the most time of Phase 1, 2, and 3 and is the largest clinical trial in the patient population. It aims to confirm earlier studies, monitor (rare) side effects, and compare with current treatment options (if available). With a Phase 0 study, your chance of reaching this phase with an effective compound is higher, and therefore a positive outcome is much more certain.